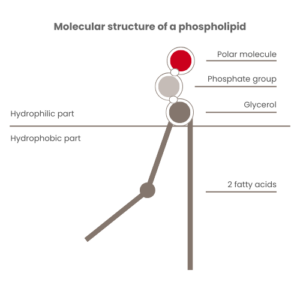
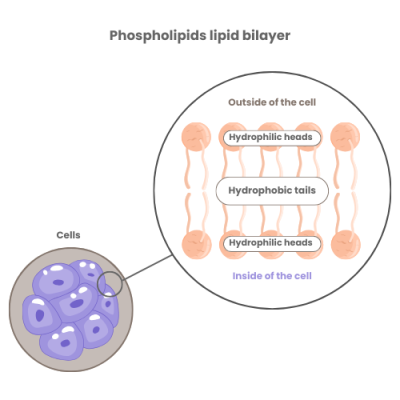
Involvement in the Functioning of Certain Organs
Phospholipids play specific roles depending on the organ.
In the liver: they contribute to the proper functioning and stability of hepatic cells. Phosphatidylcholine is the main source of choline for the liver. It plays a key role in fat metabolism, is essential for the formation and transport of lipoproteins that help remove fats from the liver, and helps maintain the integrity and stability of cell membranes in hepatic cells.
In the brain: they are involved in the structure of neurons and ensure the fluidity of nerve cell membranes. Phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylserine provide the choline and serine needed by the brain to support communication between nerve cells.